Private IP Address
A private IP address is assigned to an instance's network-interface by the DHCP server. The address is visible from within the instance by using a command like “ip a”. The address is typically part of a private network and is used for communication between instances in the same broadcast domain via virtual switch (L2 agent on each compute node). It can also be accessible from instances in other private networks via virtual router (L3 agent).
Floating IP Address
A floating IP address is a service provided by Neutron. It's not using any DHCP service or being set statically within the guest. As a matter of fact the guest's operating system has no idea that it was assigned a floating IP address. The delivery of packets to the interface with the assigned floating address is the responsibility of Neutron's L3 agent. Instances with an assigned floating IP address can be accessed from the public network by the floating IP.
A floating IP address and a private IP address can be used at the same time on a single network-interface. The private IP address is likely to be used for accessing the instance by other instances in private networks while the floating IP address would be used for accessing the instance from public networks. How to configure floating IP range describes Floating IP range document.
Example
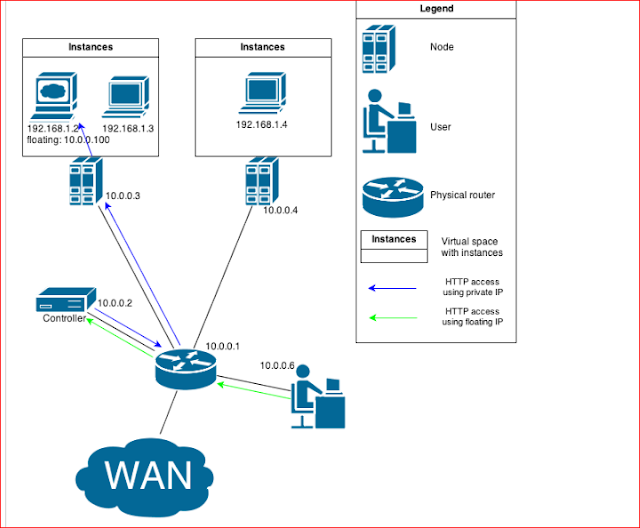
A setup with 2 compute nodes, one Neutron controller (where the Neutron service, dhcp agent and l3 agent run), a physical router and a user. Let the physical subnet be 10.0.0.0/24. On the compute nodes instances are running using the private IP range 192.168.1.0/24. One of the instances is a webserver that should be reachable from a public network. Network outline:
As shown in the picture above, the webserver is running on an instance with private IP 192.168.1.2. A User from network 10.0.0.0/24 wants to access the webserver but he's not part of private network 192.168.1.0/24. Using floating IP address 10.0.0.100 enables the user to fetch webpages from the webserver. The destination address is translated by the NAT table (iptables) within the virtual router deployed on the controller.
As shown in the picture above, the webserver is running on an instance with private IP 192.168.1.2. A User from network 10.0.0.0/24 wants to access the webserver but he's not part of private network 192.168.1.0/24. Using floating IP address 10.0.0.100 enables the user to fetch webpages from the webserver. The destination address is translated by the NAT table (iptables) within the virtual router deployed on the controller.
thanks for sharing informative information.
ReplyDelete